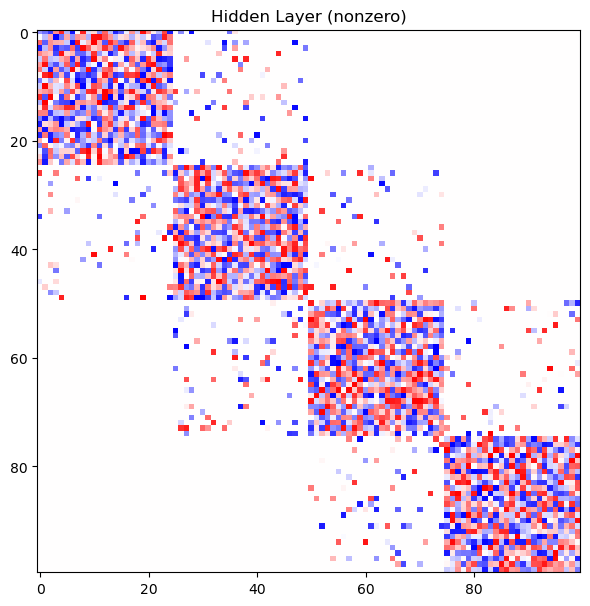
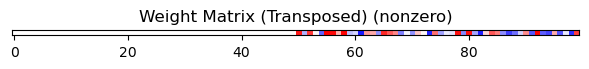
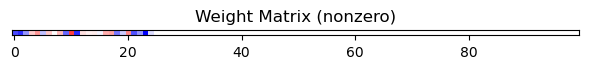mask.MultiArea
Description
This will generate a multi-area RNN without E/I constraints. Therefore, by default, the input/hidden/readout masks are binary masks. Use cautious when the positivity_constraints parameter of CTRNN is set to True, because it will make all neurons to be excitatory.
NOTE: This also implicitly covers single area case. If n_area is set to 1. All other parameters that conflict this setting will be ignored.
Parameters
n_areas(int or list, default:2):
The number of areas in the network. Can be an integer (equal-sized areas) or a list specifying the size of each area.- If an integer, the
hidden_sizemust be divisible byn_areas. - If a list, the sum of its elements must equal
hidden_size.
- If an integer, the
area_connectivities(list or np.ndarray, default:[0.1, 0.1]):
Defines the connectivity between areas.- If a list: Can have length 2 or 3:
[lower_triangle, upper_triangle, diagonal](if length 3).[lower_triangle, upper_triangle](diagonal defaults to1).
- If an np.ndarray: Must be a square matrix of shape
(n_areas, n_areas).
- If a list: Can have length 2 or 3:
-
input_areas(list or np.ndarray, optional, default:None):
Specifies the areas that receive input. Defaults to all areas ifNone. readout_areas(list or np.ndarray, optional, default:None):
Specifies the areas that send output to the readout layer. Defaults to all areas ifNone.
Methods
get_input_indices()
Returns the indices of neurons in the hidden layer that receive input.
Returns:
np.ndarray: Indices of neurons receiving input.
Usage:
input_indices = multi_area.get_input_indices()
get_non_input_indices()
Returns the indices of neurons in the hidden layer that do not receive input.
Returns:
np.ndarray: Indices of neurons not receiving input.
Usage:
non_input_indices = multi_area.get_non_input_indices()
get_readout_indices()
Returns the indices of neurons in the hidden layer that send output to the readout layer.
Returns:
np.ndarray: Indices of neurons sending readout.
Usage:
readout_indices = multi_area.get_readout_indices()
get_all_area_indices()
Returns the indices of neurons in all areas.
Returns:
list[np.ndarray]: A list of arrays, where each array contains the indices of neurons in a specific area.
Usage:
all_area_indices = multi_area.get_all_area_indices()
get_area_indices(area)
Returns the indices of neurons in a specified area.
Parameters:
area(int or str):
Area identifier. If a string, it should match one of the names returned byget_areas().
Returns:
np.ndarray: Indices of neurons in the specified area.
Usage:
area_indices = multi_area.get_area_indices(0)
get_areas()
Returns a list of area names in the format "area_{i+1}".
Returns:
list[str]: Names of areas.
Usage:
areas = multi_area.get_areas()
get_specs()
Returns the specifications of the multi-area network, including inherited specs and multi-area-specific parameters.
Returns:
dict: Specifications including:"dims""hidden_size""input_dim""readout_dim""n_areas""area_connectivities""input_areas""readout_areas"
Usage:
specs = multi_area.get_specs()
Forward Backward Specifications
RNNs can be implemented in various ways, in this library,
\(s W^T + b\)
is used in the HiddenLayer forward pass, where $W$ is the connectivity matrix of the HiddenLayer and $s$ is the current HiddenLayer state.
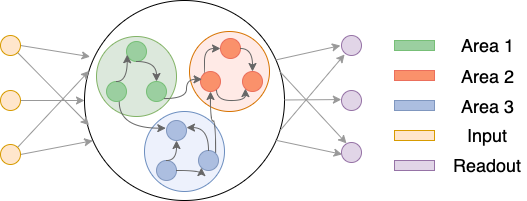
$W$ may not matter if your connectivity matrix is symmetric. But if it’s not, you might want to pay attention to the forward connections and backward connections. In the figure below, three networks (n_areas = 2, 3, 4) and their corresponding forward/backward connection matrix are provided. The blue regions are intra-area connectivity, the green regions are forward connections, and the red regions are backward connections.
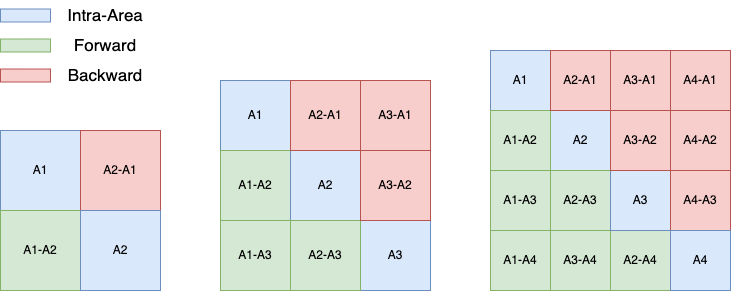
Example
from nn4n.mask import MultiArea
area_connectivities = np.array([
[1.0, 0.1, 0.0, 0.0],
[0.1, 1.0, 0.1, 0.0],
[0.0, 0.1, 1.0, 0.1],
[0.0, 0.0, 0.1, 1.0],
])
mask_params = {
"n_areas": 4,
"area_connectivities": area_connectivities,
"input_areas": [0],
"readout_areas": [2, 3],
"dims": [1, 100, 1],
}
network_mask = MultiArea(**mask_params)
network_mask.plot_masks()
Output:
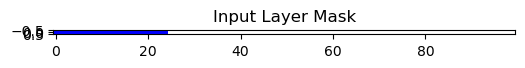
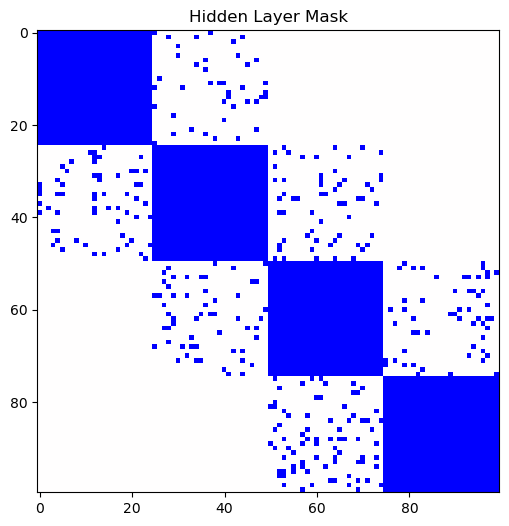
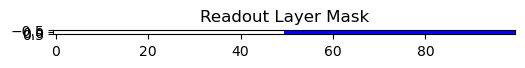
Use It as a Sparsity Mask
from nn4n.model import CTRNN
rnn = CTRNN(sparsity_masks=network_struct.get_masks())
layer = rnn.layers[1]
optimizer = torch.optim.Adam(rnn.parameters(), lr=0.001)
rnn.plot_layers()
Output: