Methods
CTRNN.eval( )
Description
Set the network to training mode, training will be performed and constraints will be enforced. Also, during training, the recurrent noises won’t be added.
Usage
import torch
from nn4n.model import CTRNN
ctrnn = CTRNN()
inputs = torch.rand(100, 1)
ctrnn = CTRNN()
for _ in range(100):
ctrnn.eval()
outputs, _ = ctrnn(inputs)
CTRNN.forward( )
Description
The forward pass of the CTRNN model. As CTRNN is a child class of torch.nn.Module, it can be called either using ctrnn.forward() or ctrnn(), where ctrnn is a instance of CTRNN.
Parameters
x: (torch.Tensor), required. The input tensor to the CTRNN model. The shape of the input tensor should be(seq_len, batch_size, input_dim).
Returns
outputs: (torch.Tensor) The output tensor of the CTRNN model. The shape of the output tensor is(seq_len, batch_size, output_dim). Note: when batch_size is 1, the shape of the output tensor is(seq_len, 1, output_dim).
hidden_states: (torch.Tensor) The hidden state tensor of the CTRNN model. The shape of the hidden state tensor is(seq_len, batch_size, hidden_dim). Note: when batch_size is 1, the shape of the hidden state tensor is(seq_len, 1, hidden_dim).
Usage
import torch
from nn4n.model import CTRNN
ctrnn = CTRNN()
outputs, hidden_states = ctrnn(torch.rand(100, 1))
# or
outputs, hidden_states = ctrnn.forward(torch.rand(100, 1))
CTRNN.load( )
Description
Load the CTRNN model from a .pth file. All model parameters and attributes will be loaded.
Parameters
path: (str), required. The path to save the model. Must end with.pth.
Usage
from nn4n.model import CTRNN
ctrnn = CTRNN()
ctrnn.load('ctrnn.pth')
CTRNN.print_layers( )
Description
Print out all layer details of the CTRNN.
Usage
from nn4n.model import CTRNN
ctrnn = CTRNN()
ctrnn.print_layers()
Output
Linear Layer:
| input_dim: 1
| output_dim: 100
| dist: uniform
| bias: True
| shape: torch.Size([100, 1])
| weight_min: -0.9917911291122437
| weight_max: 0.9899972677230835
| bias_min: 0.0
| bias_max: 0.0
| sparsity: 1
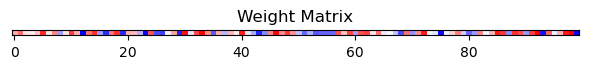
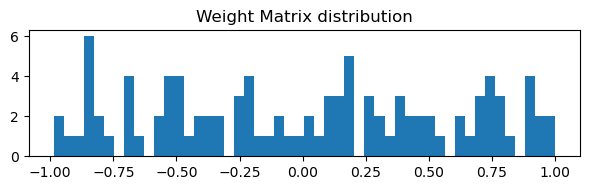
Recurrence:
| hidden_min: 0.0
| hidden_max: 0.0
| hidden_mean: 0.0
| preact_noise: 0
| postact_noise: 0
| activation: relu
| alpha: 0.1
Hidden Layer:
| self_connections: False
| input/output_dim: 100
| distribution: normal
| bias: True
| dale: False
| shape: torch.Size([100, 100])
| weight_min: -0.3491513133049011
| weight_max: 0.3499620854854584
| weight_mean: -0.0004077071789652109
| bias_min: 0.0
| bias_max: 0.0
| sparsity: 0.9900000095367432
| scaling: 1.0
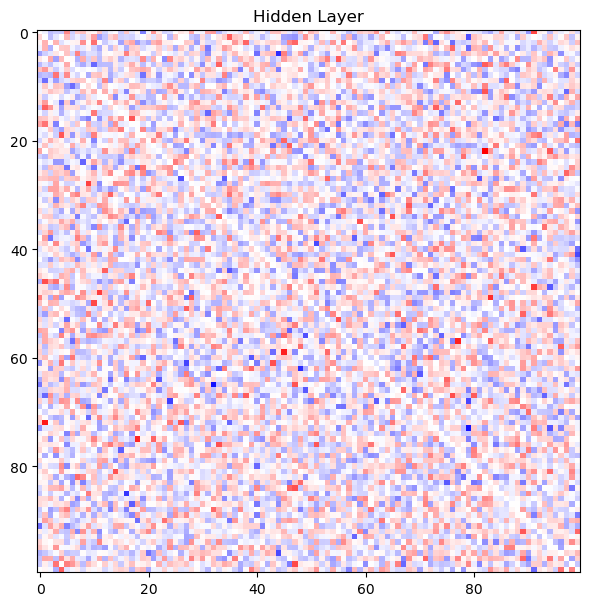
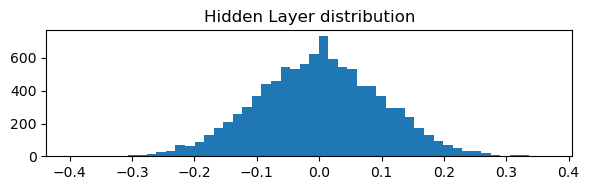
Linear Layer:
| input_dim: 100
| output_dim: 1
| dist: uniform
| bias: True
| shape: torch.Size([1, 100])
| weight_min: -0.09865634888410568
| weight_max: 0.0993180200457573
| bias_min: 0.0
| bias_max: 0.0
| sparsity: 1
CTRNN.save( )
Description
Save the CTRNN model to a .pth file. All model parameters and attributes will be saved.
Parameters
path: (str) required. The path to save the model. Must end with.pth.
Usage
from nn4n.model import CTRNN
ctrnn = CTRNN()
ctrnn.save('ctrnn.pth')
CTRNN.train()
Description
Set the network to training mode, training will be performed and constraints will be enforced. Also, during training, the recurrent noises (preact_noise and postact_noise) won’t be added.
Usage
import torch
from nn4n.model import CTRNN
inputs = torch.rand(100, 1)
targets = torch.rand(100, 1)
ctrnn = CTRNN()
optimizer = torch.optim.Adam(rnn.parameters(), lr=0.001)
for _ in range(100):
ctrnn.train()
outputs, _ = ctrnn(inputs)
loss = torch.nn.MSELoss()(outputs, targets)
optimizer.zero_grad()
loss.backward()
optimizer.step()
CTRNN.layers
Description
Get a list of the network layers.
Returns
layers: (list) A list of the network layers.
Usage
from nn4n.model import CTRNN
ctrnn = CTRNN()
layers = ctrnn.layers
for layer in layers:
print(layer)
Output
LinearLayer()
HiddenLayer()
LinearLayer()